In the face of the formidable global health challenge posed by cancer, Quantaras emerges as a key player in revolutionizing cancer treatment. The gravity of the situation is underscored by staggering statistics: According to the World Health Organization, cancer was responsible for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020, with its prevalence and incidence showing considerable variation across different regions, largely due to varying risk factors and disparities in access to healthcare. The economic impact of this disease is equally alarming, with an estimated global cost of about $1.16 trillion in 2010, a figure that encompasses not only the direct medical costs but also the indirect expenses related to lost productivity and the wider psychosocial repercussions.
Within this context, Quantaras stands at the forefront of integrating healthcare needs with technological advancement. The company specializes in enhancing the precision of cancer treatment through cutting-edge imaging technologies, including MRI, CT, and PET/CT scans. Its flagship offering, the Quantaras ContourCompanion, epitomizes this innovative spirit. This tool is designed to refine treatment planning, a critical aspect that directly influences patient outcomes and alleviates the strain on healthcare systems. By focusing on accuracy and efficiency, Quantaras significantly contributes to improving cancer care, positioning itself as an indispensable ally in the global fight against one of the most significant health crises of our era.
Founded on May 26, 2013, Quantaras was established by Joe Camaratta, a visionary in the field of medical technology. The company is headquartered in the vibrant city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, a region renowned for its rich history and dynamic innovation landscape. Situated in the Greater Philadelphia Area, which is part of the Great Lakes and Northeastern US regions, Quantaras benefits from being in a hub that’s known for its strong healthcare and technology sectors.
Pain point addressed
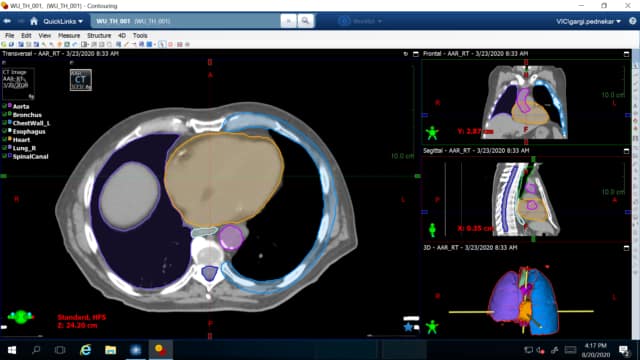
Quantaras specifically addresses a critical pain point in the cancer treatment process: the precise imaging and delineation of tumors and surrounding structures, crucial in radiotherapy planning, particularly for the head, neck, and thorax regions. This challenge predominantly affects oncology departments at the initial stages of treatment planning, involving radiologists, radiation oncologists, and medical physicists. These professionals grapple with the time-intensive and error-prone task of accurately contouring cancerous tissues and organs at risk, a process where precision is paramount to patient outcomes. Quantaras’s innovative solution, particularly through its Quantaras ContourCompanion product, revolutionizes this aspect by employing AI-driven auto-contouring. This advancement not only enhances accuracy and consistency in treatment planning but also significantly reduces the time and variability associated with manual contouring. The impact of this technology is profound, directly benefiting patients through more tailored and effective treatment plans and aiding healthcare professionals by streamlining a critical component of the cancer care process.
Type of solution
Quantaras offers a solution that falls into the category of a digital, or software-based, system. Their primary product, the Quantaras ContourCompanion, is an FDA-cleared, cloud-based, software-only medical device. This tool utilizes advanced algorithms, particularly in the realms of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, to perform auto-contouring of organs at risk in cancer treatment, focusing on the head, neck, and thorax regions.
This software-centric approach positions Quantaras in the realm of digital healthcare solutions, emphasizing the use of sophisticated computational techniques to enhance medical imaging analysis. By operating as a cloud-based platform, it allows for flexibility and scalability, providing access to powerful computing resources without the need for substantial hardware investments by the end-users, typically healthcare providers.
Type of input data leveraged
- Medical imaging data
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans.
- PET/CT (Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography) scans.
- Digital imaging data in standard formats (e.g., DICOM).
- Patient-specific information
- Anatomical details relevant to the scanned region (Head, Neck, Thorax).
- Historical imaging data for comparative analysis.
- Radiological annotations
- Existing radiologist annotations on scans.
- Oncologist notes relevant to imaging.
- Treatment planning data
- Information from radiation therapy plans.
- Dosimetric data relevant to targeted cancer treatment areas.
- Demographic data (de-identified for privacy):
- Age and gender (for anatomical variability considerations).
- General health information relevant to cancer type and treatment.
Key technology involved
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
- These AI algorithms are adept at interpreting complex medical images and identifying and learning patterns within vast datasets. The machine learning models are particularly crucial, as they continually evolve by learning from new data, thus improving their predictive capabilities and accuracy over time. This aspect of technology is instrumental in the automated analysis and interpretation of MRI, CT, and PET/CT scan data, leading to more precise treatment planning.
Computer vision
- This technology plays a pivotal role in how Quantaras’s solutions function. It enables the automatic recognition and delineation of tumors and surrounding critical structures within the imaging data. This technology is particularly essential for accurate auto-contouring of organs at risk, especially in sensitive areas such as the Head, Neck, and Thorax. By precisely identifying these areas, Quantaras aids clinicians in planning treatments that target cancerous tissues while sparing healthy ones.
Cloud computing
- The use of cloud computing in Quantaras’s infrastructure allows for the efficient handling of the extensive data involved in medical imaging. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and accessibility, ensuring that large volumes of imaging data can be processed and analyzed swiftly, regardless of the healthcare provider’s location. This approach also facilitates secure storage and sharing of data, which is crucial in collaborative treatment planning.
Data analytics
- This is another cornerstone of Quantaras’ technology approach. This involves dissecting and interpreting complex patient and imaging data to provide actionable insights. Such analytics are critical in decision-making, offering a comprehensive view that combines patient history, current imaging, and predictive analytics to guide treatment planning.
Key applications of solution
Diagnostic assistance
- Early detection: The technology’s ability to analyze and interpret complex imaging data plays a crucial role in identifying cancerous tissues at their earliest stages. This early detection is vital for improving patient prognosis.
- Precision diagnostics: By providing detailed insights from medical images, Quantaras enhances the accuracy of cancer diagnoses, ensuring that oncologists have a clear understanding of the disease’s extent and nature.
Treatment planning
- Personalized treatment approaches: Leveraging detailed imaging data, Quantaras’s solutions enable clinicians to design treatment plans that are highly tailored to individual patient needs and conditions, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
- Radiation therapy planning: The auto-contouring feature is particularly beneficial in radiation therapy, where it ensures that radiation doses are accurately targeted to tumors, thereby minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Patient monitoring
- Treatment progress tracking: Regular and precise imaging enables continuous monitoring of how a patient responds to treatment, allowing for timely adjustments in therapy.
- Post-treatment surveillance: After treatment, the technology aids in monitoring patients for any signs of cancer recurrence, ensuring prompt intervention if needed.
Enhanced radiology workflow:
- Streamlining radiologist workload: By automating the time-consuming process of contouring images, Quantaras significantly reduces the workload of radiologists, allowing them to focus on more critical tasks.
- Increasing consistency and accuracy: Automation minimizes the variability and potential for error inherent in manual image interpretation, leading to more consistent and accurate diagnoses.
Implications for key stakeholders
Patients
- A patient with head and neck cancer undergoes treatment planning using Quantaras’s technology. Traditionally, this process could be fraught with uncertainty due to the complex anatomy of this region. However, with Quantaras’s precise imaging and auto-contouring capabilities, the patient receives a highly personalized treatment plan. This precision not only increases the likelihood of successful treatment but also significantly reduces the risk of radiation-induced damage to critical structures like the salivary glands, thus preserving the patient’s quality of life.
Healthcare providers (Radiologists, Oncologists):
- In a busy oncology center, radiologists and oncologists often grapple with the time-intensive task of contouring for radiation therapy. Quantaras’s automated contouring technology streamlines this process, freeing up these professionals to focus more on patient care and less on the technicalities of image processing. This shift not only enhances the efficiency of treatment planning but also reduces the potential for burnout among healthcare providers, leading to improved job satisfaction and better patient care.
Insurers
- An insurance company, when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of different cancer treatments, finds that treatments planned with Quantaras’s technology have a higher upfront cost due to the advanced imaging analysis. However, they also notice a decrease in long-term costs due to more effective treatments, fewer complications, and a reduced need for repeat procedures. This realization could lead to more favorable coverage policies for treatments using Quantaras’s technology, benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Regulatory bodies
- A regulatory body, like the FDA, interested in promoting innovation while ensuring patient safety might view Quantaras’s FDA-cleared technology as a benchmark for future approvals. The precision and efficacy demonstrated by Quantaras could set new standards for what is expected in medical imaging technologies, influencing future regulatory policies and guidelines.
Current impact
- Clinical evaluation and collaboration: Quantaras has launched a multi-center clinical evaluation of its Automatic Anatomy Recognition (AAR) software for radiation treatment planning. This includes collaboration with institutions like the New York Proton Center, indicating a broadening reach and impact in the medical community. Such collaborations not only validate the technology but also expand its practical applications in real-world clinical settings.
- Research and development grants: The company has been awarded multiple grants, including a Phase 2 STTR grant from the National Cancer Institute for the development of its automated PET/CT interpretation software. These grants demonstrate recognition and support from significant bodies in the medical research field, underscoring the potential and efficacy of Quantaras’s technology.
- Innovative technology and benefits: The Quantaras Contour Companion offers various benefits, such as more accurate and consistent contours compared to the current standard of care, improved productivity by saving contouring time, and empowering physicians to focus more on treatment optimization. Such advancements represent a significant leap in medical imaging and treatment planning, potentially impacting a large number of patients and healthcare providers.
- Validation at academic medical centers: The application of Quantaras’s technology has been validated at several academic medical centers, indicating its reliability and effectiveness in a clinical setting. This validation is crucial for broader adoption and trust in the technology.
Potential future impact
- Expansion in clinical applications: Quantaras’s current technology, particularly the FDA-cleared Quantaras Contour Companion, focuses on the auto-contouring of organs at risk in the Head, Neck, and Thorax areas. This technology has already been validated at academic medical centers, indicating its reliability and effectiveness in clinical settings. Looking ahead, there’s potential for Quantaras to expand its applications to other body regions and cancer types, broadening its impact across the field of oncology.
- Advancement in AI and imaging technologies: Given the company’s foundational work in image processing, computer vision, and medical imaging software, there’s scope for further advancements in these areas. As AI and machine learning technologies evolve, Quantaras could integrate more sophisticated algorithms to enhance diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning precision, and patient monitoring efficacy.
- Potential for broader collaboration and research: With its roots in the Department of Radiology at the University of Pennsylvania and collaborations with institutions like the New York Proton Center, Quantaras is well-positioned to engage in more extensive research collaborations. These could involve multi-center clinical trials or partnerships with other leading cancer research centers, driving innovation and setting new standards in cancer care.
- Enhancing healthcare workflow and productivity: The benefits of Quantaras’s technology in improving productivity and empowering physicians suggest the potential for expanding its role in streamlining healthcare workflows. By reducing the time and effort required for image analysis and contouring, the technology could become integral to various healthcare settings, enhancing the efficiency and quality of care.
- Possible expansion into global markets: While the current focus appears to be within the U.S., there’s potential for Quantaras to extend its reach globally. Given the universal challenge of cancer treatment, the technology’s applicability could span diverse healthcare systems worldwide, addressing the needs of different patient populations and healthcare infrastructures.
Business model
Quantaras’s business model, centered around its advanced medical imaging technology, appears to be primarily B2B (Business-to-Business).
B2B model
- Target clients: In a B2B model, Quantaras primarily targets healthcare providers, such as hospitals, oncology centers, and specialized cancer treatment facilities. These institutions utilize Quantaras’s technology in their treatment planning and patient care processes.
- Advantages
- Stable revenue streams: Contracts with healthcare institutions can provide stable and predictable revenue streams.
- Scalability: By targeting healthcare providers, Quantaras can scale its solutions across various institutions, leveraging their networks and resources.
- Focus on core expertise: This model allows Quantaras to concentrate on product development and innovation, leaving direct patient interaction and care to healthcare providers.
Funding and key investors
Quantaras has raised a total of $2.8 million over two funding rounds, with the latest funding raised on August 9, 2018, from a Seed round. This level of funding indicates a strong interest and belief in the company’s potential from the investor community. The key investor is the National Science Foundation.
Competitive differentiator
- A key differentiator for Quantaras is its auto-contouring precision, especially in the complex regions of the Head, Neck, and Thorax. This precision is vital in radiation therapy planning, where the accurate delineation of organs at risk is crucial. The technology’s ability to navigate these intricate areas with high accuracy sets Quantaras apart and underscores its commitment to delivering solutions tailored to the most challenging aspects of cancer treatment.
- Another significant aspect is its FDA clearance combined with a cloud-based deployment model. This unique combination ensures that Quantaras’s product meets rigorous regulatory standards while offering the flexibility and accessibility of cloud technology. This blend of compliance and convenience is a distinct advantage, particularly in a healthcare landscape increasingly reliant on cloud-based solutions.
- Quantaras also excels at handling problematic cases. Its technology is adept at managing imaging data with complex characteristics, such as streak artifacts or severe pathology, demonstrating its capability to provide reliable solutions in challenging clinical scenarios. This focus on problematic cases speaks to the depth and robustness of their technology, ensuring that clinicians can trust the tool even in the most demanding situations.
Relevant regulatory and compliance requirements
FDA regulations
- In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a critical role in regulating medical devices. Solutions like Quantaras’, especially those used in diagnosis and treatment planning, must comply with FDA regulations to ensure they are safe and effective for clinical use. This includes premarket notification [510(k)], premarket approval (PMA), and compliance with the Quality System Regulation (QSR).
HIPAA compliance:
- As Quantaras’s solution handles patient data, adherence to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential. This ensures that all patient information is handled, stored, and transmitted securely, safeguarding patient privacy and confidentiality.
ISO certification:
- Obtaining ISO certification, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, can be crucial. This standard relates to the quality management system and the consistent meeting of customer and regulatory requirements, particularly for medical device manufacturers.
Case studies
“Our unique technology helps physicians make better treatment decisions by supporting recognition and analysis of anatomical structures and diseased tissue using MRI, CT, and PET/CT images.” Quantaras’ website
Areas for continuous improvements
Diversification of disease focus
- Expanding beyond current specializations to include a wider range of diseases, particularly those where advanced imaging could play a critical role, such as neurodegenerative diseases or cardiovascular conditions. This expansion would not only increase the applicability of their technology but also address a broader spectrum of healthcare needs.
Enhanced language and cultural adaptation
- Incorporating multiple language support and cultural considerations into their software is vital for global expansion. This includes adapting the user interface and support materials to different languages and cultural contexts, which could make the technology more accessible and user-friendly for diverse global markets.
Inclusive patient data sets for development:
- Ensuring the diversity of patient groups in the development and training of their AI algorithms. This includes using medical imaging data from a wide range of demographics to reduce bias and improve the applicability of the technology across different patient populations.
References
https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/quantitative-radiology-solutions
Disclaimer: Please note that the opinions, content, and analysis in my posts are entirely my own and do not reflect the views of any current or past employers or institutional affiliations. These posts, based solely on publicly available information, are for informational purposes and should not be taken as professional advice. All insights and conclusions are my viewpoints and should not be considered representative of any organizations I am or have been associated with. This content is not endorsed by, nor does it represent the stance of any affiliated entity.





